But there's more to this very cheery vitamin than meets the eye. Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium, and without it, bones are weakened. However, too much vitamin D can be toxic, especially in children. In this article, we'll discuss the importance and amounts needed for vitamin D.
Here's a brief overview:
What is Vitamin D?
Your body can make its own vitamin D with enough sunlight -- which researchers discovered when it became clear vitamin D-deficiency diseases such as rickets were rare in sunny climates. In the 1920s, rickets was prevented by feeding children cod liver oil or foods exposed to ultraviolet light. Today rickets is rare in the United States because milk is now fortified with vitamin D. Learn about vitamin D's history.
Benefits of Vitamin D
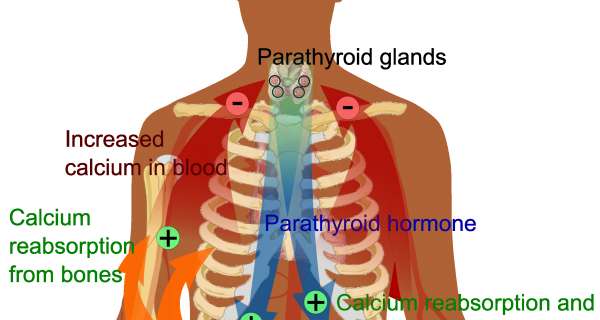
Vitamin D is needed to help the body absorb calcium and phosphorus, which help the growth of bones and teeth. In addition, vitamin D regulates whether these minerals are deposited into bone or withdrawn out of it. If minerals are drawn out more than they are put in, this can leave bones soft and weak. On this page, we'll discuss more about vitamin D's uses.
Foods That Contain Vitamin D
The foods that contain significant amounts of vitamin D naturally are not necessarily foods you want to overdo: butter, cream, egg yolks and liver. However, all milk -- including skim - is fortified with vitamin D and is an excellent source. Learn more about what foods are vitamin D sources.
Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency causes rickets or bone softening, in children, and in adults can cause osteomalacia, which involves the loss of calcium and protein from bones. Though rickets is rare in the United States today, some cases do appear in low-income and vegetarian children and infants breastfed for an extended period of time with no supplementation. Find out more about Vitamin D deficiency in this section.
Vitamin D Supplements
Adding extra vitamin D to a diet can be helpful for vegans, babies who are breastfed and people with rickets. However, too much vitamin D can be toxic, resulting in calcium deposits in the kidneys, heart and other tissues that cause irreversible damage, and therefore amounts should be carefully regulated. Check out this section for more on what supplements exist and how much is needed.
How Vitamin D Works?